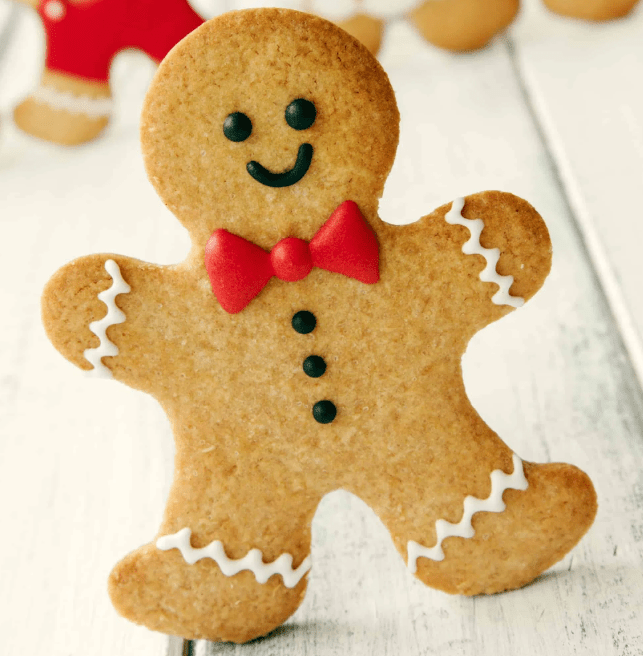A Gingerbread Biscuit With Chocolate Chips For Eyes Is Not VATable BUT With Any More Decoration, It Is VATable!
What is VAT?
VAT (or Value Added Tax, to give its full name) was introduced in the UK in 1973 and is the third largest source of government revenue after income tax and National Insurance.
VAT is levied on the sale of goods and services by UK businesses and is charged by a business at the point of sale of goods and services. The standard rate of VAT is currently 20%* and this rate has been in place since 4 January 2011. This rate covers most goods and services. The other rates are:
• Reduced rate of 5%, which covers some goods and services, such as domestic fuel or children’s car seats
• Zero rate, examples of which are children’s clothes and some foods
• Some items are exempt from VAT altogether, such as postage stamps and insurance
No VAT is charged on anything that is outside the scope of the UK VAT system
Who should register for VAT?
The threshold for a business to register for VAT is when the VAT taxable turnover exceeds £85,000* (taxable turnover is the total value of everything sold that is not exempt from VAT) there are, however, different thresholds for buying and selling from other EU countries. Businesses can voluntarily register for VAT if their turnover is below £85,000* to avoid forgetting to register.
If a business sells goods or services that are exempt from VAT or ‘out of scope’ but buy goods for more than £85,000 from EU VAT registered suppliers then the business needs to register for VAT.
To register for VAT, a business will need to contact HMRC if the business goes over the VAT threshold in a rolling 12 month period. In fact, a business should monitor its turnover regularly to check whether it will go over the threshold. The de-registration level for a business is less than £83,000*.
If you register your business for VAT late, you will need to pay what you owe from when you should have registered is and there may be a penalty for not registering.
VAT Schemes
The VAT Accrual Scheme:
- The return is calculated on the difference between the sales and purchase invoices within the relevant period
- The return does not take account of whether the sales and purchase invoices have been paid or are still outstanding
- A return is submitted to HMRC every quarter
The Flat Rate Scheme:
- Business will pay a fixed amount of VAT
- The business will retain the difference between what it pays to HMRC and what it invoices its customers for
- No VAT can be claimed on the business’s purchases, there is an exception to this, where it is possible to reclaim VAT on a single purchase of capital expenditure, where the amount of the purchase, including VAT, is over £2,000*
- The threshold for joining this scheme is £150,000*
- The scheme cannot be rejoined until 12 months after leaving
- There are incentives for the first year of registration
Cash Accounting Scheme:
- VAT is not included on the sales of a business until the customer pays the invoice
- VAT on purchases cannot be reclaimed until the purchases have been paid
- Cash Accounting is ideal for those with slow payers
- The joining threshold for this scheme is £1.35 million
Annual Accounting Scheme:
- The business will make advance VAT payments to HMRC
- These payments are based on the VAT due for the previous year or on an estimated return for a new business
- Only one VAT return is submitted each year and this will include the balance of the VAT due
- If the VAT has been overpaid, then it will be necessary to apply for a refund
- The turnover is £1.35 million for joining the scheme
- A VAT return can be submitted online and is due one calendar month and seven days after the end of the last quarter (a quarter is known as the accounting period)
- The payment also needs to reach HMRC within this time frame
There are various penalties for late submission of a VAT return, the severity of which depends on the amount of previous late submissions and the turnover of the business.
How Cashtrak Can Help
Different accounting schemes suit different types of business depending on their circumstances so we recommend talking your situation through with us so we can understand how you work to be able to suggest the right scheme for you.
The VAT rules can be complex, you are legally obliged to accurately account for VAT, business records for VAT purposes must be kept for at least 6 years. HMRC will issue penalties for late filing late payment and incorrect information on your return. Cashtrak can ensure you are compliant and claiming what is owed to you. Some of the unusual VAT examples:
If you provide your staff with an annual party (such as a Christmas party, this is an allowable expense and you can reclaim the VAT as long as the cost of the party was less than £150 per employee AND was open to all employees
A Gingerbread biscuit man or woman has no VAT applied IF it has chocolate dots for eyes but any other decoration is VATable
Frozen yoghurt is charged at the standard VAT rate BUT frozen yoghurt that is designed to be thawed before eaten is zero rated
The VAT return itself isn’t difficult, it is the work that goes on behind it to ensure compliance that takes the time. Cashtrak have many years experience with VAT work across a wide variety of business sectors so knowing which scheme is best for you and ensuring you claim what you owe and you are compliant is second nature to us.
*August 2020